L-5MTHF is the active form of folate, but ironically, it...
Read More


MTHFR A1298C is a genetic variant that affects the function of the MTHFR enzyme, which is involved in the activation of the B-vitamin folate. The A1298C variant is a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) that occurs when the DNA code for the MTHFR gene has a one-letter change from an adenine (A) to a cytosine (C) at position 1298. This genetic variation can impact the body’s ability to activate folate, which is important for DNA synthesis, repair, and the methylation process. The MTHFR A1298C variant has been associated with a range of health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, pregnancy complications, and mental health disorders. However, the significance of this variant varies depending on other genetic and environmental factors.
The frequency of the MTHFR A1298C mutation varies by ethnicity and geography. In general, it is less common than another MTHFR variant, C677T. However, the frequency of A1298C can be higher in certain populations, such as individuals of Hispanic or African ancestry. According to some studies, the frequency of the A1298C mutation can range from less than 5% to over 30% in different populations. It is important to note that having the mutation does not necessarily mean that a person will experience negative health effects, as the impact of genetic variants can depend on many factors, including diet, lifestyle and other genetic factors.
The symptoms associated with the MTHFR A1298C mutation can vary widely between individuals and may depend on several factors, including other genetic variants, diet, and environmental factors. Some people with this mutation may not experience any symptoms at all. However, some studies have suggested that the MTHFR A1298C mutation may be associated with an increased risk of certain health conditions, including:
Cardiovascular disease: Individuals with the MTHFR A1298C mutation may be at an increased risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and blood clots.
Pregnancy complications: The MTHFR A1298C mutation has been associated with an increased risk of pregnancy complications, including recurrent miscarriage and preeclampsia.
Mental health disorders: Some studies sugggest that the MTHFR A1298C mutation may be associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders.
Neurological disorders: Research suggests that the MTHFR A1298C mutation may be associated with an increased risk of neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
It is important to note that having the MTHFR A1298C mutation does not necessarily mean that a person will experience any of these symptoms, and many people with the mutation may never develop any related health problems. Additionally, many other factors, including lifestyle, nutrition, and environmental factors, can also influence a person’s risk of developing these conditions.
There is evidence to suggest that the MTHFR A1298C mutation may be associated with an increased risk of miscarriage, although the exact nature of this relationship is still being studied. One way that the mutation may contribute to miscarriage risk is by affecting the body’s ability to activate folate, which is essential for fetal development. In particular, research suggests that the mutation may impair the body’s ability to produce a form of folate called 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF), which is important for the development of the neural tube.
Some studies have found that women with the MTHFR A1298C mutation are more likely to experience recurrent miscarriage, which is defined as two or more consecutive pregnancy losses before 20 weeks of gestation. However, it is important to note that many other factors, including other genetic variants, lifestyle factors, and medical conditions, can also contribute to miscarriage risk. As with any medical concern, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you have questions or concerns about the MTHFR A1298C mutation and your pregnancy.
Many articles exist claiming that A1298C mutations have more tendency towards neurotransmitter imbalance than C677T, Also, C677T mutations are more likely to lead to high homocysteine. But as far as I can tell, this started with someone jumping to a conclusion, and then the rest of the internet echoing that same conclusion back to them without bothering to do the research.
The thing that matters, in the end, is how compromised your MTHFR enzyme is, in combination with how much folate you’re getting. As more research is completed, this idea might be refined, revised, or even overturned completely, but for now, this is it.
Just for convenience, here is a table with levels of compromise, and here are the sources I have used.
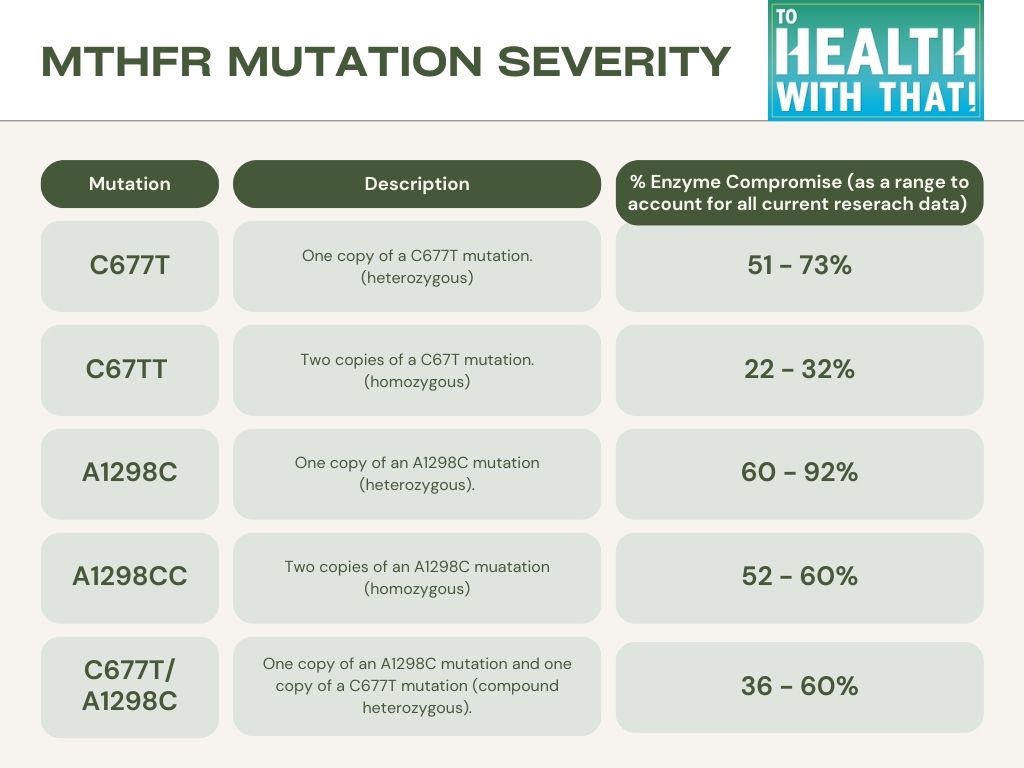
The MTHFR A1298C mutation can be detected through a genetic test, which analyzes a sample of DNA, often from a cheek swab, from the individual being tested. Genetic testing can be done through a variety of methods, including blood tests, saliva tests, or cheek swabs.
The test for the MTHFR A1298C mutation typically involves analyzing the DNA sequence of the MTHFR gene, which provides instructions for making the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. The A1298C variant refers to a specific change in the DNA sequence of the MTHFR gene, where the DNA base adenine (A) is replaced with cytosine (C) at position 1298.
Genetic testing for MTHFR A1298C is typically ordered by a healthcare provider if there is a suspicion that an individual may have the mutation, based on their personal or family medical history. It can also be discovered through genetic testing platforms such as 23andme.com or ancestry.com.
Not all individuals with the mutation will experience health problems, and not all health problems are caused by the mutation.
The MTHFR A1298C mutation is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means that an individual can inherit a good or bad copy from each parent depending on the copies that their parents naturally carry, and the effects of the mutation are stronger with more mutated copies present.
If both parents carry one copy of the mutated MTHFR gene and one normal or “wild type” gene, there is a 25% chance with each pregnancy that their child will inherit two copies of the mutated gene. There is a 50% chance that their child will inherit one copy of the mutated gene, and a 25% chance that their child will inherit two copies of the normal gene.
It is important to note that many individuals who carry one or two copies of the MTHFR A1298C mutation may never experience any related health problems. Additionally, other genetic and environmental factors can also influence the expression of the mutation and the associated health risks. If you are concerned about the inheritance of the MTHFR A1298C mutation or any other genetic condition, speak with a healthcare provider or a genetic counselor, who can provide personalized advice based on your individual situation.
The MTHFR A1298C mutation affects the activity of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) enzyme, which is involved in the activation of folate, a B-vitamin that is important for many biological processes in the body.
Individuals with the MTHFR A1298C mutation may have reduced activity of the MTHFR enzyme, which can lead to decreased amount of folate being converted to the active form, and therefore impaired folate status. This is because the mutation affects the enzyme's ability to convert 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, which is a critical step in folate metabolism. As a result, folate may not be properly utilized by the body, leading to potentially elevated homocysteine levels and decreased methylation capacity.
Decreased folate status and impaired folate metabolism have been linked to a number of health conditions, including birth defects, cardiovascular disease, certain cancers, and neurological disorders such as depression and dementia.
Many factors, including other genetic variants and environmental factors, can also contribute to these conditions. Additionally, not all individuals with the MTHFR A1298C mutation will experience health problems, and the degree of impairment can vary depending on a variety of factors.
There is some evidence to suggest that the MTHFR A1298C mutation may also affect vitamin B12 metabolism, which is another essential nutrient that is involved in many biological processes in the body.
Vitamin B12 is important for the maintenance of healthy nerve cells and red blood cells, as well as for DNA synthesis and energy production. Like folate, vitamin B12 is involved in the process of methylation, which is important for regulating gene expression and other cellular processes.
Research suggests that the MTHFR A1298C mutation can be associated with lower vitamin B12 status. This may contribute to the development of certain health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and neurological disorders.
However, the relationship between the MTHFR A1298C mutation and vitamin B12 is complex and not fully understood. More research is needed to clarify the potential impact of the mutation on vitamin B12 metabolism and its role in the development of various health conditions.
The MTHFR A1298C mutation can affect homocysteine levels in the body. Homocysteine is an amino acid that is normally recycled into methionine, another amino acid, with the help of the MTHFR enzyme.
Individuals with the MTHFR A1298C mutation may have reduced activity of the MTHFR enzyme, which can lead to decreased conversion of homocysteine to methionine. As a result, homocysteine levels may become elevated in the blood, a condition known as hyperhomocysteinemia.
Elevated homocysteine levels have been linked to an increased risk of various health problems, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, and certain neurological disorders. However, it is important to note that many factors, including other genetic variants and environmental factors, can also contribute to these conditions.
Managing homocysteine levels is important for health, and treatment options may include increased intake of MTHFR-safe forms of folate and other B-vitamins, such as vitamin B6 and vitamin B12.
Individuals with the MTHFR A1298C mutation may need to pay extra attention to their folate and vitamin B intake to help manage homocysteine levels. If you are concerned about your homocysteine levels or any other health condition, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
There is currently no specific treatment for MTHFR A1298C mutation, as it is a genetic condition that cannot be cured. However, there are steps that individuals with the mutation can take to manage their health and reduce the risk of associated health conditions.
One of the most important steps is to maintain a healthy and balanced diet that is rich in nutrients, particularly folate and other B-vitamins such as vitamin B6 and vitamin B12. These nutrients are important for proper methylation and can help support overall health and well-being. Also, avoiding foods fortified with folic acid or supplemental folic acid, the synthetic form of folate, can be extremely helpful as this form is associated with “pseudo-MTHFR” in too high doses.
In some cases, individuals with the MTHFR A1298C mutation may benefit from taking supplements of MTHFR-safe forms of folate like folinic acid or 5-LMTHF and other B-vitamins, although this should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
For individuals with elevated homocysteine levels, treatment options may include increased intake of MTHFR-safe forms of folate and other B-vitamins, as well as other lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, smoking cessation, and stress reduction.
The impact of the MTHFR A1298C mutation on health outcomes can vary widely depending on individual factors such as lifestyle, other genetic variants, and environmental exposures. If you are concerned about your health or have questions about the MTHFR A1298C mutation, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet that is rich in nutrients, particularly folate and other B-vitamins, can be beneficial for overall health and well-being for individuals with MTHFR mutations. Also, avoiding foods fortified with folic acid and avoiding folic acid in supplements is extremely helpful as this form of folate has been shown to be detremental to those with MTHFR mutations.
Foods that are high in natural, MTHFR-safe folate include leafy green vegetables, beans, lentils, asparagus, citrus fruits, and avocados. In some cases, individuals with the MTHFR A1298C mutation may benefit from taking supplements of MTHFR-safe forms of folate like folinic acid or 5-LMTHF along with other B-vitamins, although this should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It is also important for individuals with this mutation to avoid lifestyle factors that may increase the risk of associated health conditions, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can also help support overall health and well-being.
If you have concerns about your diet or any other aspect of your health, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional for personalized advice, or schedule a free 15 minute consult with Dr. Amy for MTHFR basics
MTHFR A1298C mutation is a genetic condition that cannot be cured. However, there are steps that individuals with the mutation can take to manage their health and reduce the risk of associated health conditions. This may include maintaining a healthy MTHFR-safe diet including lots of fruits, vegetables, beans, and legumes and reducing exposure to foods fortified with synthetic folic acid, which is not appropriate for people with an MTHFR mutation. It may also include supplements of MTHFR-safe forms of folate including folinic acid and 5-LMTHF and other B-vitamins, and avoiding lifestyle factors that may increase the risk of health problems like smoking, excessive drinking, and street drugs.
It is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan for managing the condition and promoting overall health and well-being, or schedule a free 15 minute meet and greet appointment with Dr. Amy to see if you are a good fit to work together: MTHFR basics
L-5MTHF is the active form of folate, but ironically, it...
Read MoreDetoxifying is incredible for your body, so why does it...
Read MoreL-5MTHF is the active form of folate, but ironically, it...
Read MoreDetoxifying is incredible for your body, so why does it...
Read More